0769-23388351
Toggle Navigation
Neodymium magnets are a very widely used type of rare-earth permanent magnets. Due to their extremely high magnetic properties, neodymium magnets have a wide range of applications in industry and daily life. However, the magnetic properties of neodymium magnets are sensitive to temperature, so understanding their temperature limitations is essential for use and storage.
Temperature Performance of Neodymium Magnets
Neodymium magnets have an extremely high magnetic energy product (BHmax) at room temperature, which makes them the strongest commercially available magnets. Their strong magnetic properties have led to a wide range of applications in electronics, motors, sensors and medical devices. However, one of the main drawbacks of neodymium magnets is their sensitivity to temperature.
Curie temperature is the temperature at which a material loses its magnetic properties. For neodymium magnets, the Curie temperature is usually between 310°C and 370°C. Above this temperature, neodymium magnets will completely lose their magnetic properties. This is an irreversible process and the magnet cannot regain its magnetic properties even after cooling.
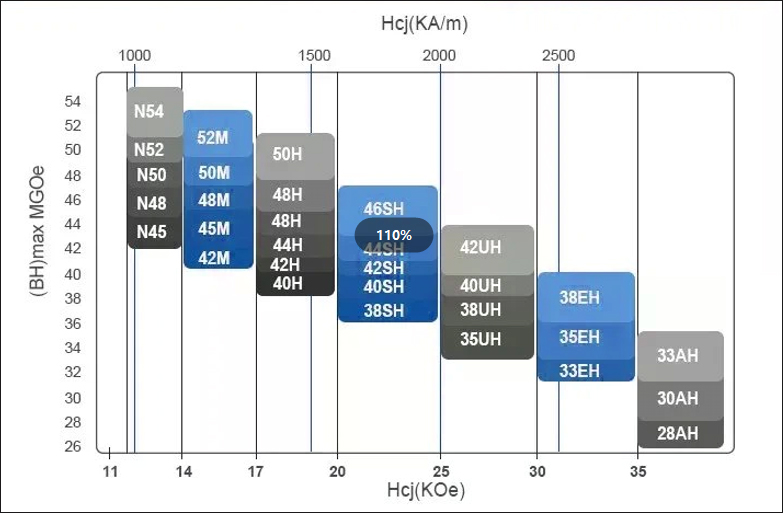
The maximum operating temperature is the highest temperature at which a magnet can continue to operate without significant loss of magnetic properties. For neodymium magnets, this temperature range is usually between 80°C and 230°C, depending on the grade of magnet. Different grades of neodymium magnets have different temperature stability. For example, N35 magnets have a maximum operating temperature of about 80°C, while N52 magnets have a maximum operating temperature of about 60°C. High-temperature grades of neodymium magnets, such as H, SH, UH, EH, and AH, have maximum operating temperatures that can reach 150°C to 230°C.
Neodymium Magnet Grade Characteristics Table
The performance of neodymium magnets at high temperatures decreases mainly in the following aspects:
1. Decrease in coercivity (Hc): The coercivity of neodymium magnets decreases with increasing temperature. This means that magnets are more easily demagnetized at high temperatures.
2. Decrease in Magnetic Flux Density (Br): Higher temperatures cause a decrease in the residual magnetic flux density of neodymium magnets, which reduces their magnetic field strength.
3. Decrease in magnetic energy product (BHmax): The magnetic energy product of neodymium magnets also decreases significantly at high temperatures.
In some applications, neodymium magnets inevitably need to work in high temperature environments. For example, in electric cars and wind turbines, the motor generates a lot of heat when it works, and the magnet must be able to withstand these high temperature environments. To solve this problem, the following measures can be taken:
1. Selection of high-temperature grade magnets: according to the specific application requirements, select appropriate high-temperature grade magnets, such as SH, UH, EH, etc.
2. improve the cooling system: add cooling system in the equipment design to ensure that the magnet working temperature does not exceed its maximum working temperature.
3. Use alternative materials: In extreme high temperature environments, consider using other types of magnets, such as samarium cobalt (SmCo) magnets, which have better high temperature performance, but slightly lower magnetic properties than neodymium magnets.
Related articles added;
Neodymium Working Temperature Range (Rating)
Temperature coefficient and characteristic curve of neodymium magnet
Neodymium round magnets with a diameter of 5mm and a thickness of 4mm are more commonly used. If you feel that the magnetic force is not enough, the performance level can be appropriately improved. Welcome to consult the price!...
Our company is a permanent magnet supplier from China. We are good at processing micro-precision magnets, high-performance magnets, special-shaped magnets, and multi-pole ring magnets. The quality is guaranteed and the price is not expensive. We look forward to customer consultation from all over the world....
The sample is an N52 high-performance ultra small hole radially sintered neodymium rotor magnet, with specifications of 2mm outer diameter, 0.9mm bore, and 4.5mm height....
This is a square neodymium magnet for earphones, the length and width are 5mm, the thickness is 2mm, the thickness is magnetized, the surface is galvanized, 1mm or other thickness can also be selected, non-high temperature grade, the maximum working temperature is less than 80 ℃...
The sample is a high-performance ferrite rotor magnet with a radial 3-pair pole configuration (6 poles), measuring 20mm in outer diameter, center bore diameter of 8mm, and height of 27mm. surface magnetic flux density reaches approximately 1800 Gauss....
This is a small-sized short bar shaped neodymium iron boron strong magnet with a specification of 1.5 × 1.5 × 10mm. It is made of N42 performance grade neodymium iron boron material and magnetized along the length direction (10 mm direction)....
This is a rare earth NdFeB strong magnet with a length of 30mm, a width of 20mm and a thickness of 10mm. Surface treatment is nickel-copper-nickel, and the thickness is 10mm. Magnetization direction is length direction....
This product is a small rare earth NdFeB magnet ring, with gold plated surface, N52 grade, the magnetization method is axial, the size is 5mm outer diameter, 2mm inner hole, 2mm height, and the tolerance can be ±0.02mm. Welcome to consult us for the price....